Create a Simple Face Swap App with Python and Streamlit
Written on
Overview of the Face Swap Application
In this tutorial, we will explore how to create an application that swaps real faces with generated ones using the Face Swap and StyleGAN projects. This is a fun and innovative way to utilize artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies to create engaging visuals.

AI's Role in Face Generation
Artificial intelligence and machine learning have gained immense popularity and are utilized for various applications, including the generation of non-existent individuals.
Imagine encountering a person who isn't real!
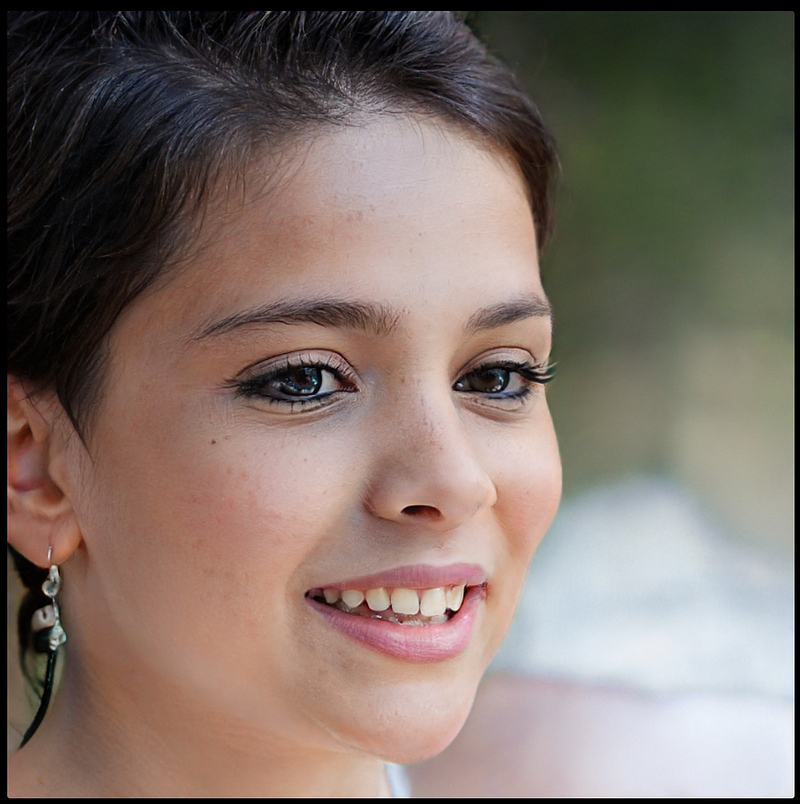

This image was produced by StyleGAN, a tool for generating fake individuals.
Utilizing Generated Faces
Here are some practical applications for the generation of fake faces:
- Developing an AI algorithm that can differentiate between real and artificial faces by creating extensive dummy datasets for training.
- If you’re planning to sell items online, featuring a model wearing your clothes can enhance your advertisement's appeal. You can swap your face with a generated one to maintain anonymity.
- For marketing presentations, hiring models can be costly, and many online images are copyrighted. Opting for a generated image could be a cost-effective alternative.
In this article, you will learn how to:
- Generate fake individuals using the StyleGAN algorithm.
- Use the Face Swap Python project for seamless face swapping.
- Create a simple web interface with the Streamlit library to upload images and perform face swaps.
- Deploy your application to Streamlit Cloud and share it with friends.
Let’s get started!
Understanding the Technology
Introduction to StyleGAN
StyleGAN is an open-source project that employs deep learning techniques to generate realistic human faces with diverse gender and ethnic backgrounds.
For further insights into the algorithm, check out the project on GitHub.
Overview of Face Swap
Face Swap is a publicly available Python project that allows users to interchange faces in images, videos, and even live streams. All you need are a source and target image, and the code will produce a blended result.
Streamlit Explained
Streamlit is an open-source framework for rapidly creating and deploying web applications using Python. It is especially popular among data scientists, as it requires no prior front-end development skills, making it easy to learn.
Preparing Your Project
Now that you know where to source your fake faces, let’s generate new images based on given source and target photos.
Begin by executing the following commands to install the necessary requirements for Face Swap:
$ cd FaceSwap
$ python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt
Generating a resultant image is as simple as running this command:
python3 main.py --src {source.jpg} --dst {target.jpg} --out {result.jpg} --correct_color --no_debug_window
Explanation of Command Arguments
- --src: Path to the source image.
- --dst: Path to the target image.
- --out: Path where the result will be saved.
- --correct_color: Aims to enhance the color realism of the output image.
- --no_debug_window: Suppresses the debug window.
Script Output Example:
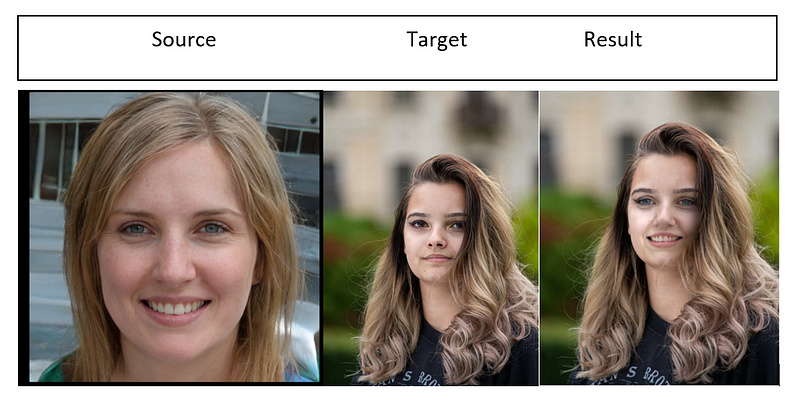

Source image by StyleGAN, Target image by @patrikvelich
Deploying Your Application
Until now, we have been using the terminal to run the Python script for face swapping. However, it would be more user-friendly to create a web interface for image uploads.
To achieve this, we will utilize the Streamlit API to develop a basic UI for the Face Swap code. The simplest method is to fork the GitHub repository and modify the main.py file.
For brevity, I will not include the original code here, but you can view it in the References section below. Here is the modified version:
Code Modifications
Key changes include:
- Adding Streamlit and PIL dependencies.
- Implementing file upload buttons in the UI using st_uploader.
- Converting the PIL image to OpenCV format with cv2.cvtColor(numpy.array(source_image), cv2.IMREAD_COLOR), as the original code requires OpenCV format.
- Displaying the output image using st.image(output, width=500).
Next, update the requirements.txt file with the necessary libraries for Streamlit.
Choose your app's GitHub repository and click deploy:
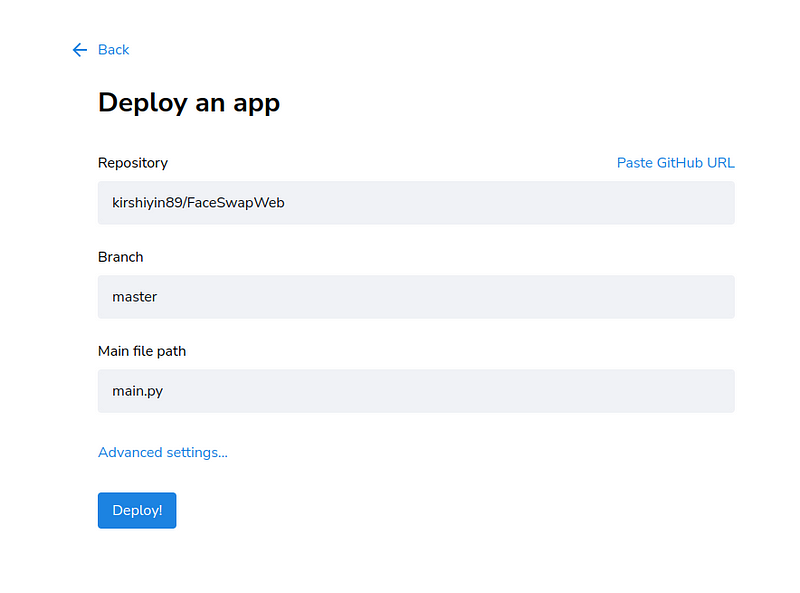
Your deployment will take a few moments. Grab a coffee while you wait, and soon you’ll have your new app ready to use.
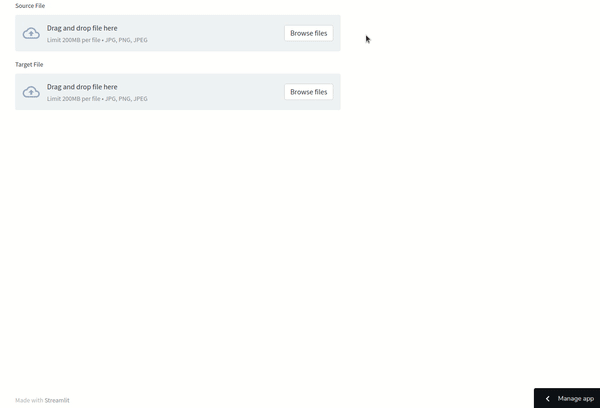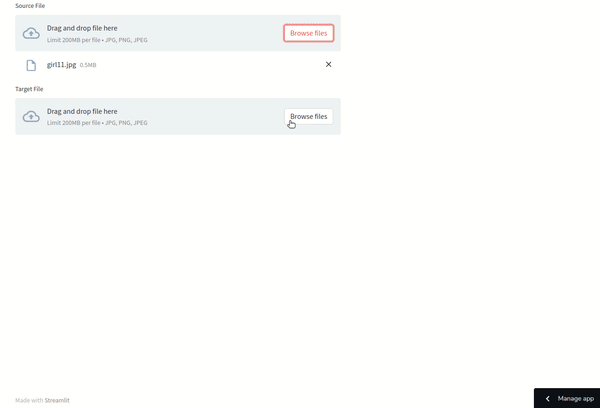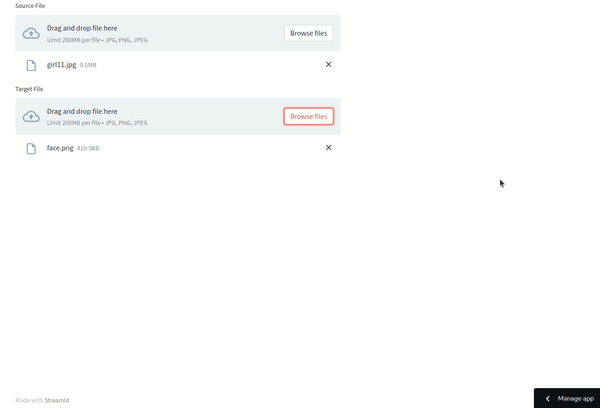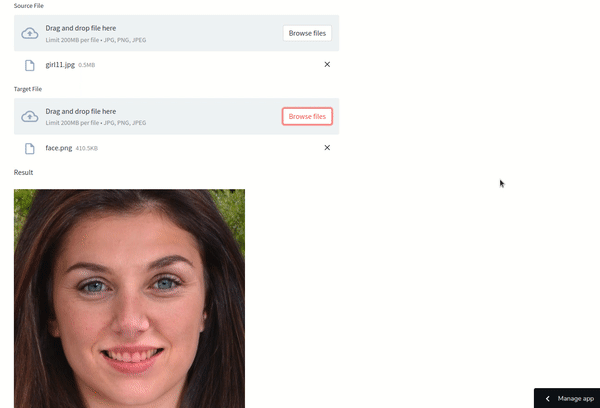
The results are impressive! For optimal outcomes, select source and target images that share similar lighting and poses. If needed, you can refine the results using photo editing software like Photoshop.
Click on the "Share" button to send your app link to friends, allowing them to try it out in their browsers.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you have learned a straightforward method to generate and swap faces using the Face Swap and StyleGAN projects. You also discovered how to deploy and share your web application using Streamlit.
The user interface is minimal for demonstration purposes, but I encourage you to explore Streamlit's API to enhance it further.
Thank you for reading, and happy coding!
References
Adding Video References
To further enhance your understanding, check out these informative videos:
Unbelievable Face Swapping with 5 Lines Code - This video showcases an impressive technique for face swapping with minimal code, offering a great starting point for developers.
Building a Machine Learning App in Python with Streamlit - This video provides insights on creating web applications using Streamlit, which will be beneficial for your app deployment process.