DNA Hydrogels: A Revolutionary Approach to Data Storage
Written on
Chapter 1: The Need for Innovative Data Storage Solutions
In today's digital landscape, the demand for data storage has escalated dramatically. Traditional storage solutions like hard drives and magnetic tapes are nearing their capacity limits, struggling to accommodate the ever-increasing need for storage space.
Enter the promising realm of DNA data storage. This groundbreaking technology utilizes the ancient genetic code to offer an innovative solution characterized by unparalleled data density and durability.
Section 1.1: The Potential of DNA Storage
DNA molecules, as you may know, operate on a four-letter code comprising A, T, C, and G. Theoretically, DNA can hold an astonishing amount of data—up to 10 billion times more than conventional storage systems—boasting a density of approximately 455 exabytes per gram. Nonetheless, several challenges must be addressed before realizing this potential.
Currently, DNA powder is a common medium for DNA data storage. However, it presents certain challenges:
- DNA powder requires additional protective carriers, such as silica beads, which diminish the effective storage capacity.
- It is vulnerable to damage and contamination.
- The need for stabilizers further reduces the storage capability and complicates the mixing process.
As of now, the highest recorded data storage within a DNA medium used magnetic nanoparticles, achieving around 10 gigabytes (one exabyte) per gram. Yet, difficulties arose during the DNA retrieval process, rendering it unsuitable for repeated use.
Subsection 1.1.1: Enter Hydrogels
Hydrogels are three-dimensional polymeric networks capable of retaining significant amounts of water. Researchers are now investigating the use of hydrogels for DNA storage solutions.
To facilitate this, a Python program was developed, allowing for quick and efficient conversion between digital information and DNA sequences. This innovative program enables coding in just 0.21 seconds and decoding in a mere 0.26 seconds.
The researchers opted to utilize TRFG (thermally responsive functionally graded) hydrogels for their DNA storage. Essentially, they start with a liquid, filling it with long-chain molecules made of repeating units (polymers). By modifying the types of polymers used, the properties of the hydrogel can be adjusted. In this case, a positively charged polymer network was created in the gel to "load" the negatively charged DNA.
A key feature of this polymer blend is its sensitivity to temperature and pH. By elevating either the temperature or pH, the DNA can be released for reading. This method is non-destructive, making it potentially reusable.
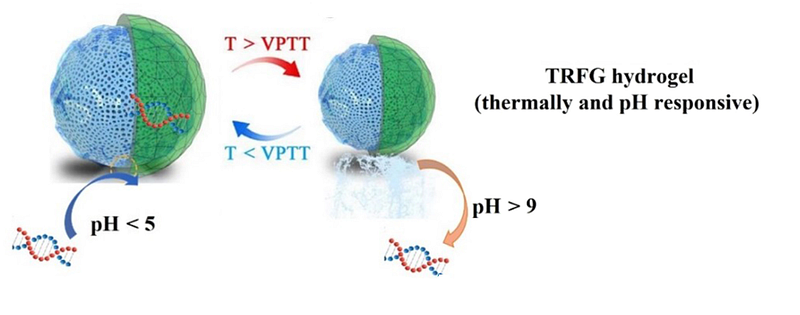
The researchers achieved a remarkable milestone by successfully storing 7 reusable exabytes of information in just one gram of hydrogel, setting a new record.
The researchers concluded that:
“Above all, the DNA storage system based on the TRFG hydrogels significantly enhances DNA data density, long-term accuracy, recovery, and ease of use. Given these attributes, our newly synthesized TRFG hydrogels hold tremendous potential for DNA storage applications.”
Chapter 2: Exploring the Future of DNA as a Storage Medium
The first video titled "Is DNA the Future of Data Storage?" delves into the potential of DNA as a revolutionary medium for storing vast amounts of information.
The second video, "Introducing DNA Data Storage with the DNA Data Storage Alliance," provides insights into the collaborative efforts aimed at advancing DNA storage technologies.