Understanding Canine Vision: How Dogs Perceive Their World
Written on
Chapter 1: The Unique Perspective of Dogs
Have you ever wondered why a dog struggles to spot a red ball against white snow? This intriguing question highlights the differences between canine and human vision.
Not yet a member? Enjoy free access here!
Did you know that dogs experience their surroundings in a way that is completely different from humans? In this article, we will explore how a dog might perceive the image below.
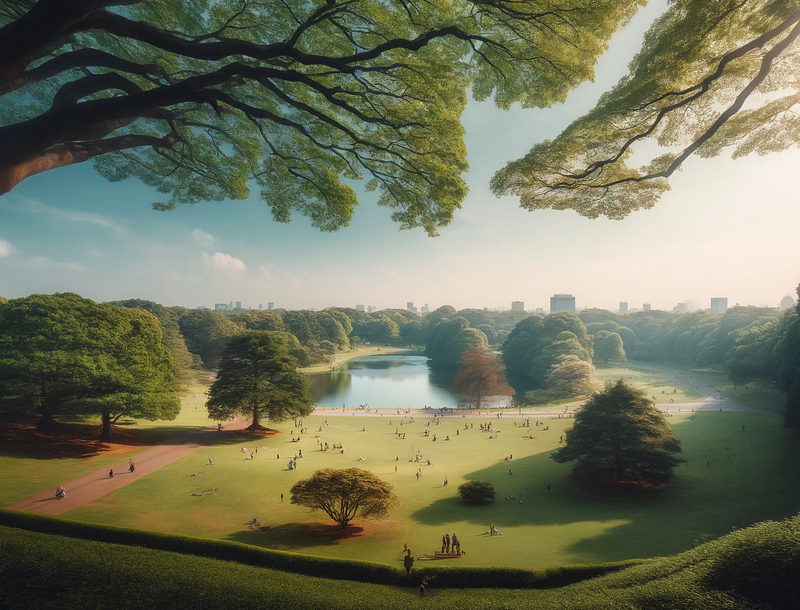

Field of Vision
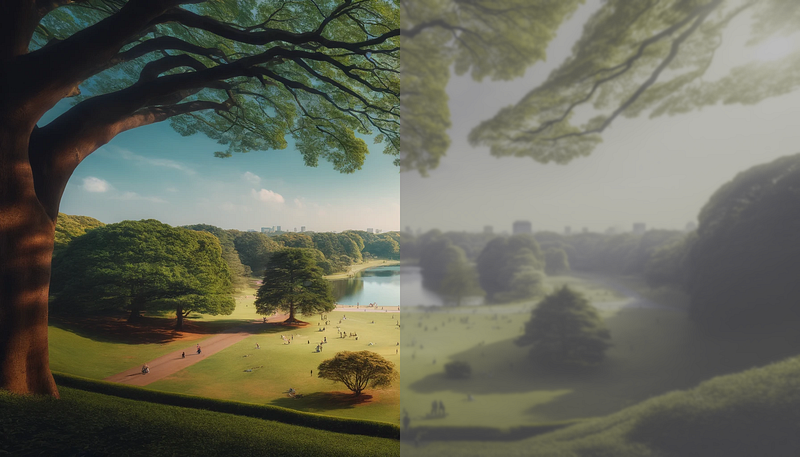
One of the primary distinctions between dogs and humans lies in our respective fields of vision. Humans typically have a field of view of around 180 degrees, which limits our ability to see what’s behind us. In contrast, dogs enjoy a much broader field of vision, approximately 240 degrees.
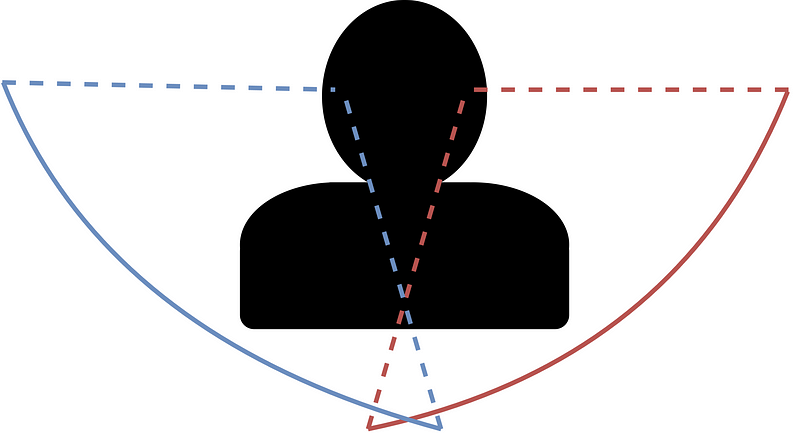
Human vs. Dog Field of View
The average human can see within a range of 180 degrees, while dogs can see about 30% to 40% more, reaching up to 240 degrees. The images below illustrate this difference.

Color Vision
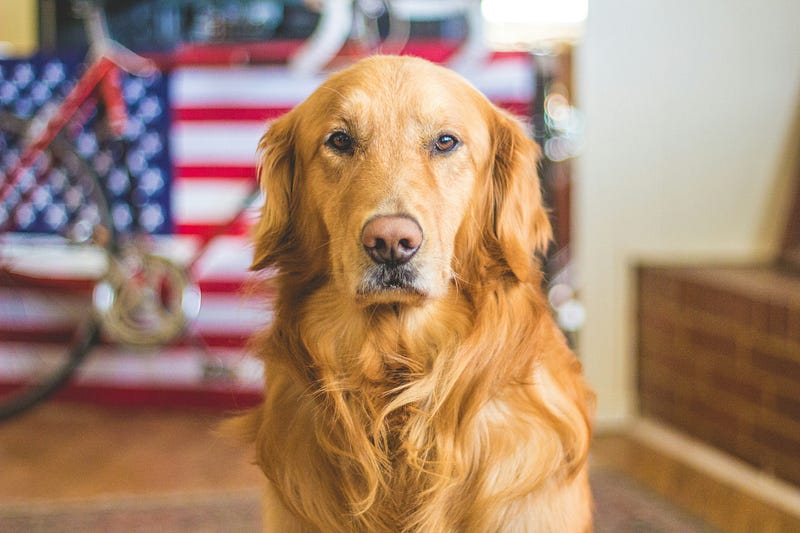
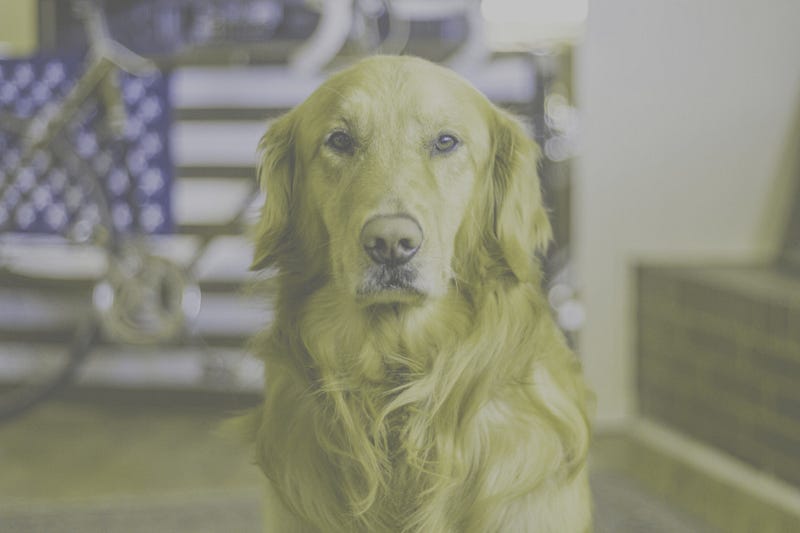
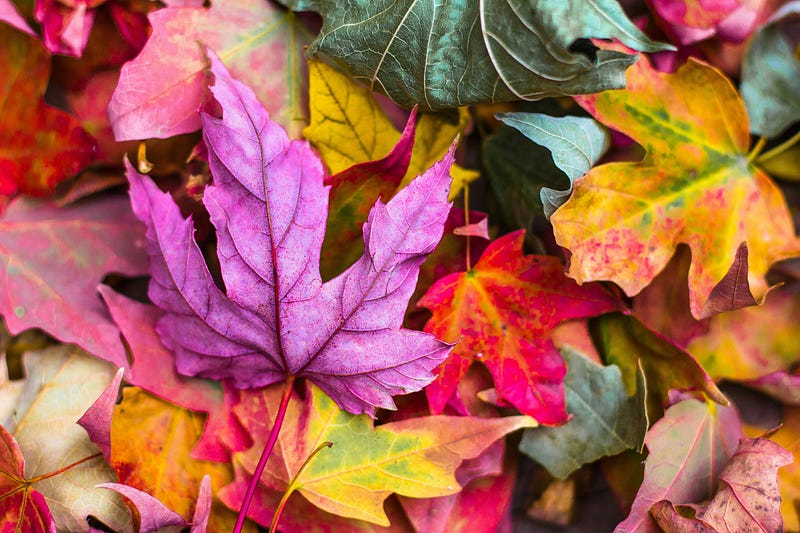
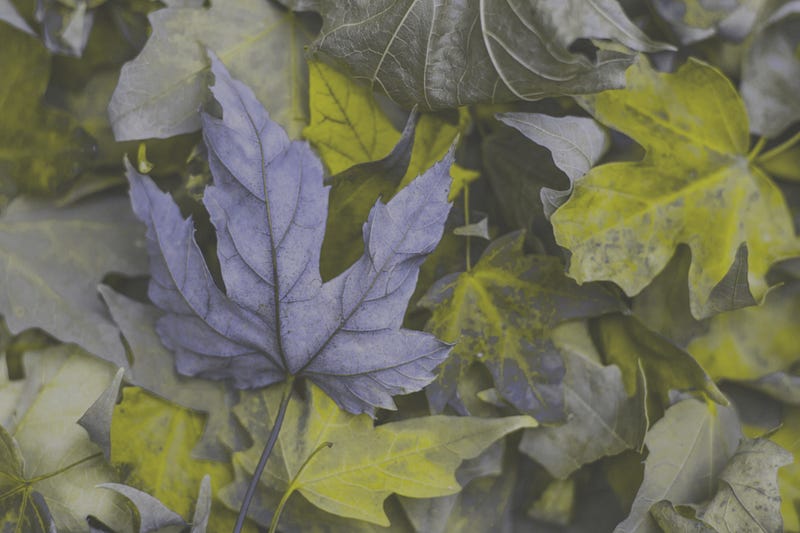
Another notable difference is in color perception. Humans generally possess three types of photoreceptors in our eyes, known as cones. Dogs, on the other hand, have only two types. As a result, their ability to perceive color is significantly more limited, primarily recognizing shades of blue and yellow.
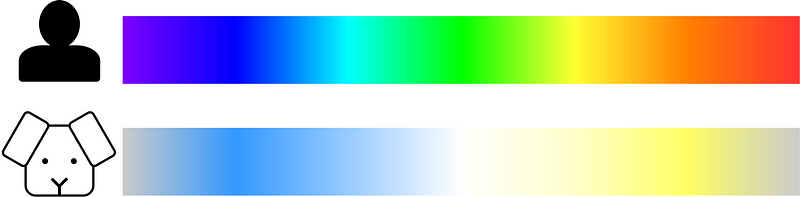
Human vs. Dog Color Spectrum
With their two photoreceptors, dogs are capable of seeing blue and yellow light, but they struggle to distinguish red and green—similar to the experience of humans with red-green color blindness. The following image highlights this difference more vividly.

Near-Sightedness
In terms of distance vision, dogs are more nearsighted than humans. While an average person can see clearly from a distance of about 23 meters (75 feet), a dog’s clear vision extends only to approximately 6 meters (20 feet).
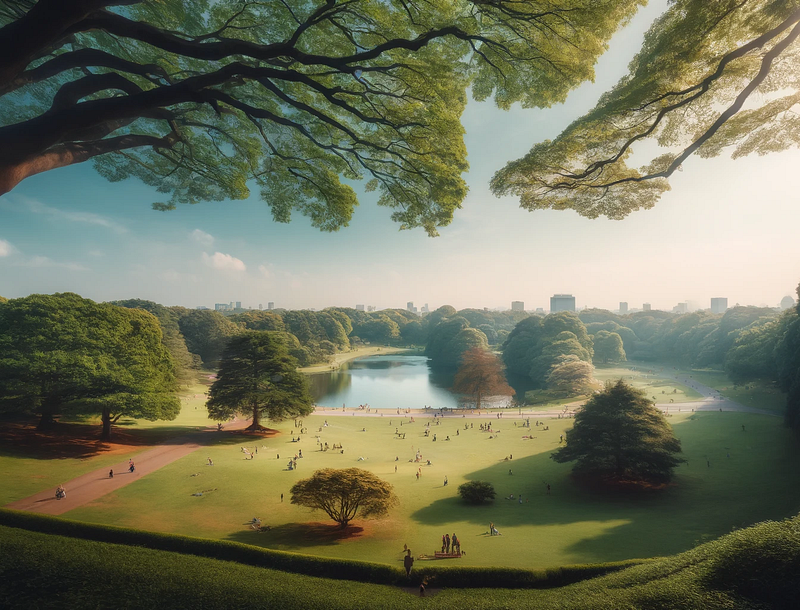

Human vs. Dog Near-Sightedness
To illustrate this contrast, we can apply a blurriness effect to the image below, showcasing the difference in clarity between human and dog vision.
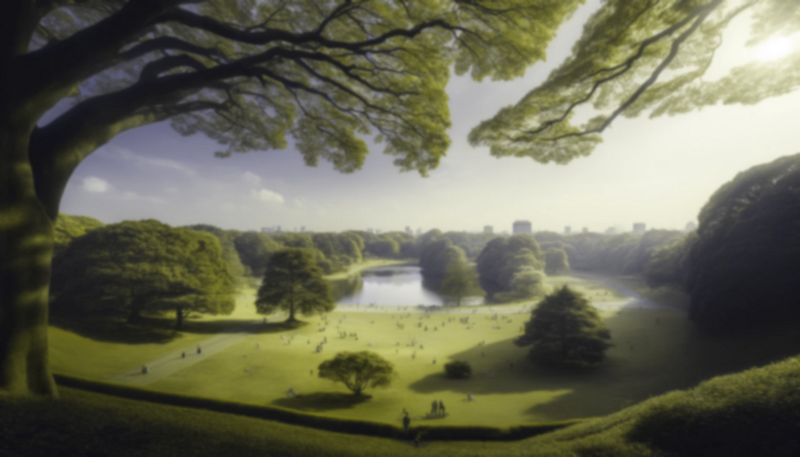

Contrast Perception
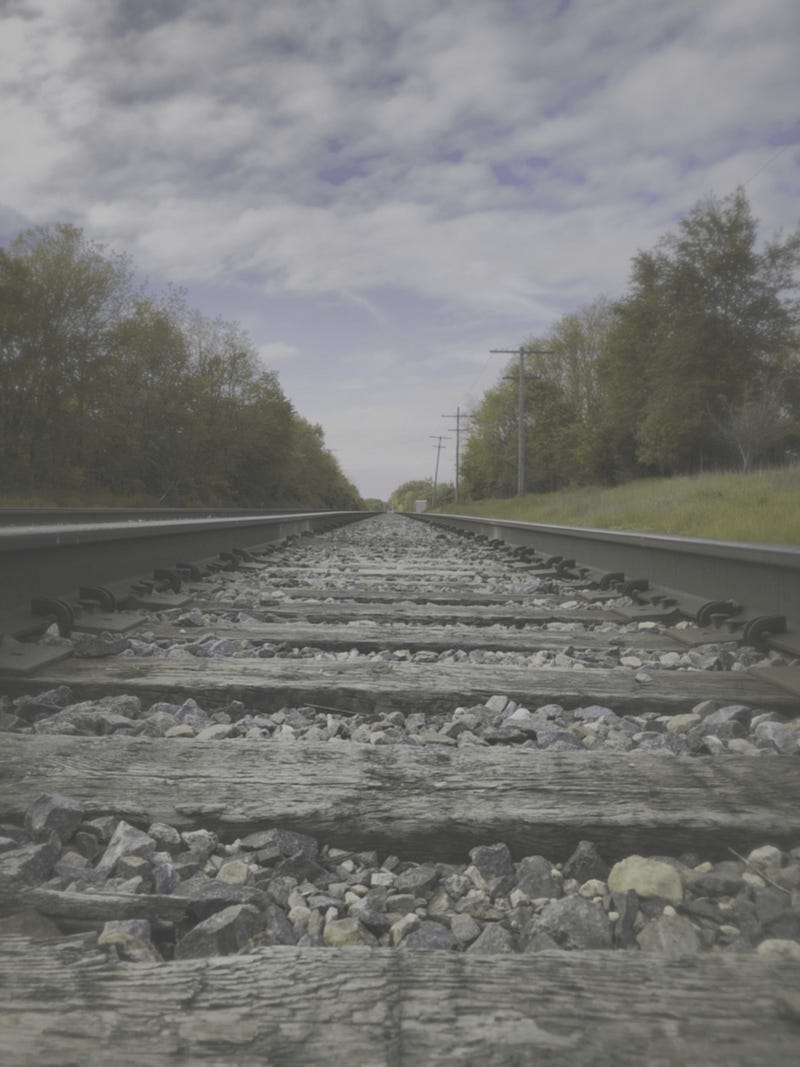
Dogs also perceive contrast differently, leading to a less distinct separation between objects and their backgrounds. This reduced contrast makes it challenging for dogs to differentiate between shadows and actual objects.
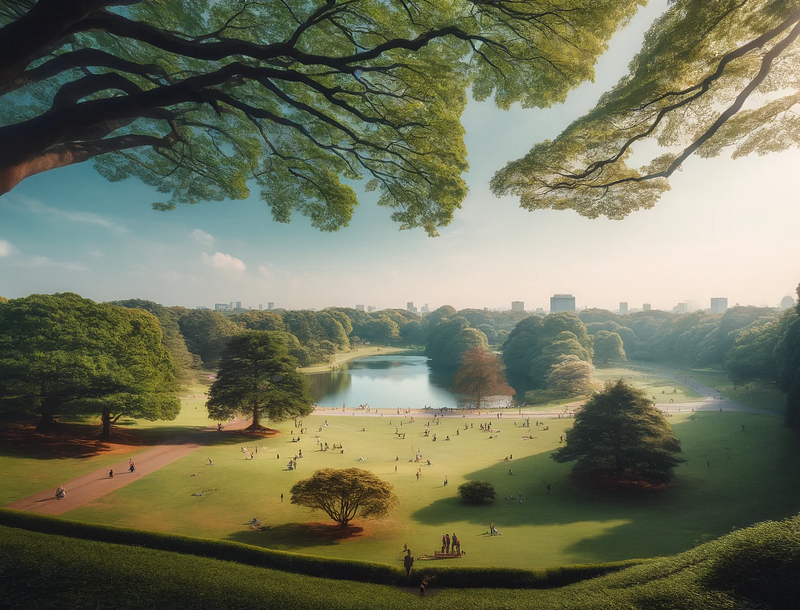

Human vs. Dog Contrast
The image below depicts how this lack of contrast impacts a dog's ability to locate objects effectively.
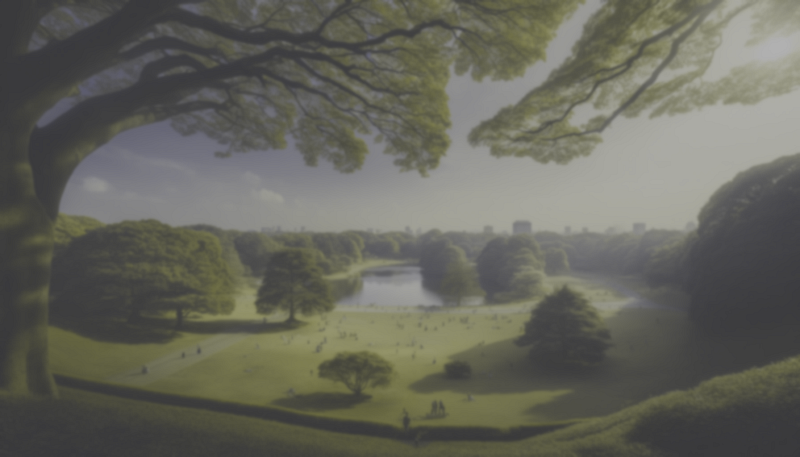

Comparison of Vision
So, why do dogs have difficulty finding a red ball in white snow? The image below illustrates the differences between human and dog vision, without considering the field of view.

Additional Images
Here are more visuals that further explore the contrasts between human and canine vision.







More on Canine Experiences
Here are additional stories related to our canine companions:
- Transforming Cats into Dogs Using AI
- Introducing Machine Learning to Track My Dog