# The Surprising Risks of Excessive Fish Oil Consumption
Written on
Understanding the Risks of Fish Oil
The belief that fish oil benefits health is widely accepted, backed by substantial clinical evidence. However, it’s essential to recognize that omega-3 fatty acids are highly susceptible to oxidation, which can render fish oil supplements toxic. In this regard, fish oil can be considered a double-edged sword. Another critical aspect to consider is the quantity consumed.
Is More Fish Oil Always Better?
Research conducted by the University of Sao Paulo delves into this question. The study aimed to determine whether the quantity of fish oil affects its health benefits. The experiment involved 38 mice divided into five distinct groups:
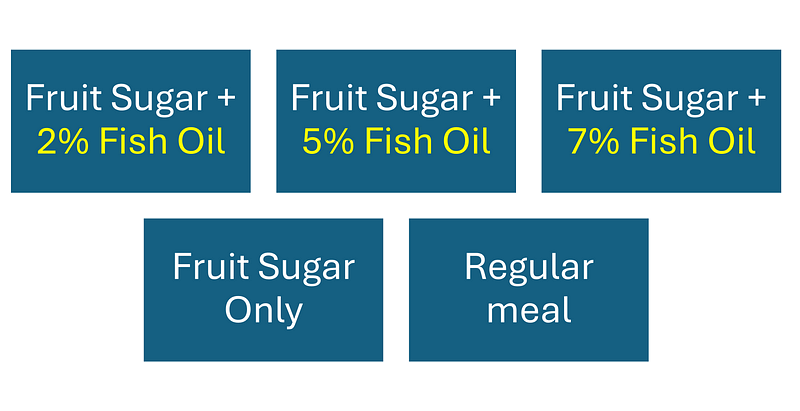
The percentage of fish oil indicates its proportion in the total diet. For instance, 2% means that 2% of the overall diet consists of fish oil.
In this investigation, the mice's livers were damaged using high levels of fructose, and then varying amounts of fish oil were administered to evaluate the outcomes.
Impact of Excessive Fish Oil Intake
Inflammatory substances act like a fire starter within the body. After 60 days, the results indicated that groups consuming 2% to 5% fish oil experienced health improvements.
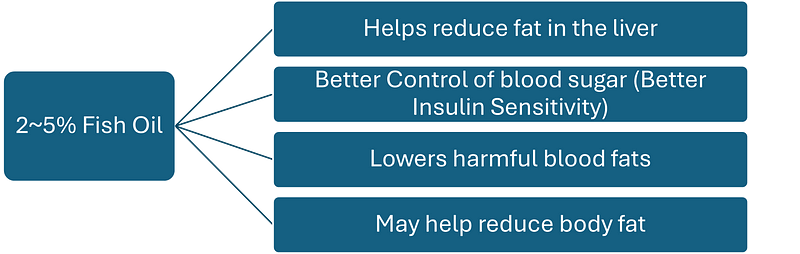
However, the group receiving 7% fish oil saw a decline in their health status.

The data suggests that while benefits increased steadily up to 5%, a detrimental effect was observed once intake surpassed 7%. For context, a 7% fish oil intake in mice equates to approximately 5g per day for humans. The underlying issue is that excessive fish oil consumption can lead to heightened inflammation in the body.
Consequences of High Fish Oil Consumption
The group that ingested 7% fish oil showed a marked deterioration in their health compared to those who did not take fish oil at all. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF-α), a cytokine that can target tumors when produced in moderation, becomes harmful when its levels rise excessively, leading to significant inflammation and accelerated aging.
When the body cannot process surplus fish oil, it oxidizes and decays internally, resulting in inflammation—an intricate and concerning mechanism.
Summary of Findings
While this study was conducted on mice, other research indicates that athletes consuming over 2g of fish oil daily reported increased oxidative stress and diminished performance. Therefore, it's prudent to approach high fish oil intake with caution.
Currently, there is no universally recognized upper limit for fish oil, but a daily intake of 2g is advisable, with 1g being a safer option for those with concerns. Given the potential harm from excessive fish oil and the oxidation issues associated with supplements, obtaining omega-3s from real fish is certainly the safer choice. Additionally, it is crucial to minimize omega-6 intake (found in vegetable oils, snacks, and fried foods).
Keep these considerations in mind when incorporating fish oil into your diet.
Chapter 2: Exploring Fish Oil Safety
The first video titled "Supplements and Safety (full documentary) | Hidden Dangers of Vitamins & Supplements | FRONTLINE" explores the potential hazards associated with vitamin and supplement intake, shedding light on safety concerns.
The second video, "The Hidden Danger of Seed Oils: Too Much Omega 6," discusses the implications of excessive omega-6 consumption and its effects on health, providing valuable insights into dietary choices.
Related Article
The alarming truth about fish oil supplements: Are they harming you?
short.sweet.pub